A Japanese consortium consisting of shipping, energy and financial companies is looking beyond the country’s borders and wants to participate in a green ammonia project in India.
Mitsui O.S.K. Lines (MOL), IHI Corporation, Hokkaido Electric Power, Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Company, Mizuho Bank and Tokyo Century Corporation have signed a letter of intent to this effect.
Together with the Indian company ACME Group, a player in the renewable energy sector, a new production plant is to be built in the eastern Indian state of Odisha by 2030. The aim is to produce around 4 lakh tons (400,000 tons) of green ammonia annually.
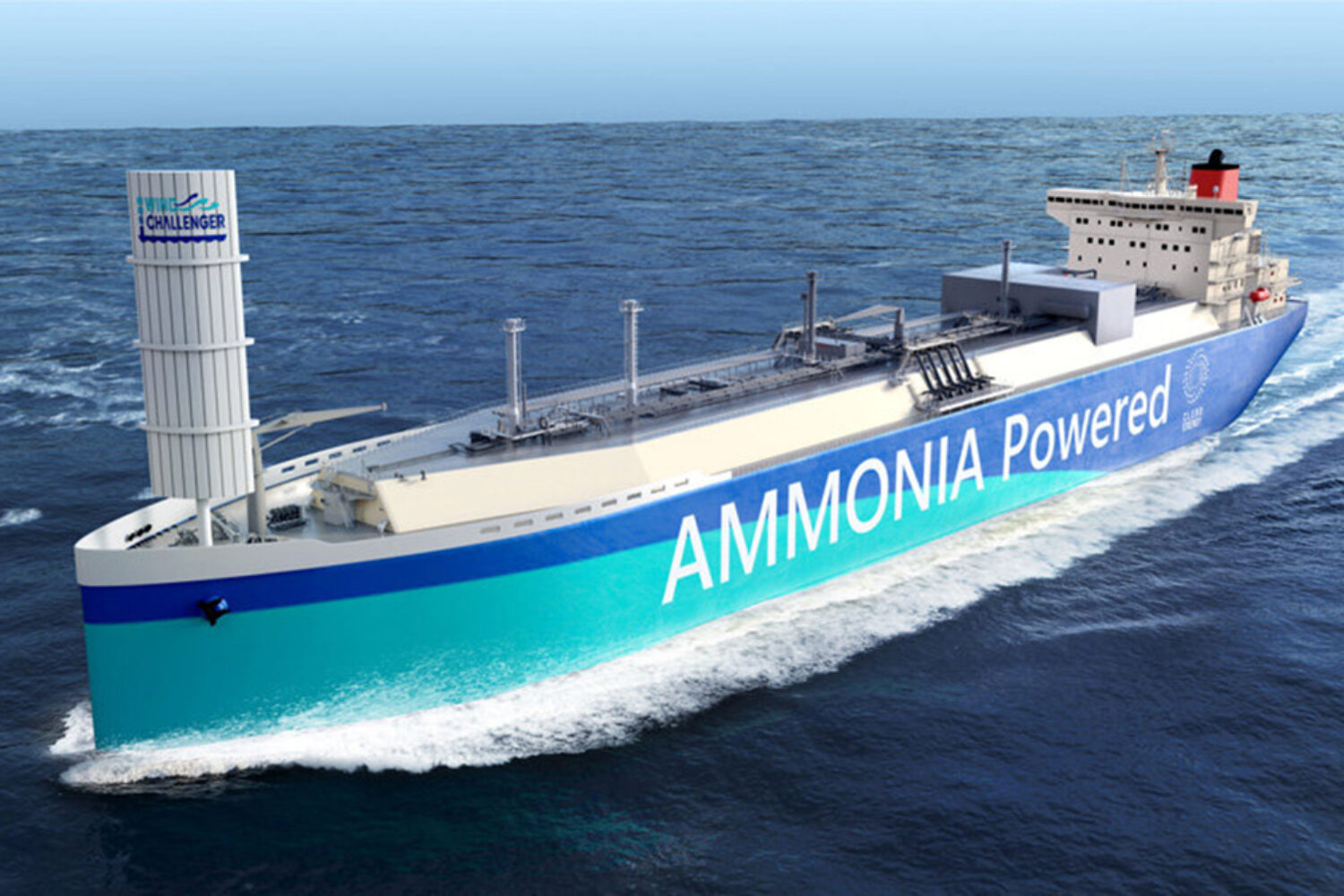
The ammonia produced will be transported to Japan in liquefied form using special ammonia tankers, where it will primarily be supplied to energy suppliers and chemical companies. Green ammonia is considered a promising – albeit risky – CO₂-free energy source that does not release any greenhouse gases when burned. Its proponents hope that it has potential as an emission-free fuel in power plants and shipping and can contribute to the decarbonization of energy-intensive industries in the long term.
Establishing an international ammonia supply chain
The initiative aims to establish a robust international ammonia value chain from production to transportation and use. The establishment of a special purpose company (SPC) is also being examined in order to bundle investments and operational processes. The six participating companies each contribute industry-specific expertise to the partnership: IHI is driving the development of Japan’s first ammonia supply chain, while MOL is building a logistics infrastructure with IHI. This will also include ocean and coastal shipping.
Hokkaido Electric Power plans to use ammonia at its coal-fired Tomatoh-Atsuma power plant and to build supply and storage infrastructure in Hokkaido. Mitsubishi Gas Chemical, which has long been active in the ammonia business, wants to contribute to the decarbonization of this raw material. Mizuho Bank is providing an investment volume of 2 trillion yen by 2030 for projects in the fields of hydrogen, ammonia and related technologies. Tokyo Century, previously active in the field of solar energy, is considering an investment to exploit the potential of green ammonia as a key component of a CO₂-neutral energy future.
The project is considered a milestone in the implementation of global climate targets and is intended to secure a stable, environmentally friendly energy supply for Japan in the long term. The country also wants to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels and move away from geopolitically unstable supply chains. (rup)